INTRODUCTION
TO MICROSOFT EXCEL
• Microsoft Excel
• Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet application in the
Microsoft Office Suite. A spreadsheet is an accounting program for the
computer. Spreadsheets are primarily used to work with numbers and text.
Spreadsheets can help organize information, like alphabetizing a list of names
or ordering records, or calculate and analyze information using mathematical
formulas.
• Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet
• is the computer equivalent of a paper ledger
sheet.
• It consists of a grid made from columns and
rows.
• It
is an environment that can make number manipulation easy and somewhat painless.
Important Terms
• A workbook is made up of three worksheets.
• The worksheets are labelled Sheet1, Sheet2, and
Sheet3.
• Each Excel worksheet is made up of columns and rows.
• In order to access a worksheet, click on the
tab that says Sheet#.
Important Terms
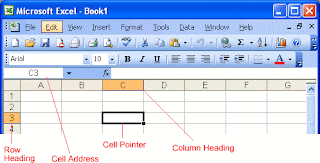
• Each cell has a unique cell address composed of
a cell's column and row.
• The active cell is the cell that receives the
data or command you give it.
• A darkened border, called the cell pointer,
identifies it.
• Basics of spread sheets
Basic of spread sheets
• Spreadsheets are made up of
1. columns
2. rows
3. and
their intersections are called cells
• In
each cell there may be the following types of data
Ø text
(labels)
Ø number
data (constants)
Ø formulas
(mathematical equations that do all the work)
• Column Headings
• Each Excel spreadsheet contains 256 columns. Each
column is named by a letter or combination of letters.
• Row Headings
• Each spreadsheet contains 65,536 rows. Each row is
named by a number.
• COLUMN
• In
a spreadsheet the COLUMN
• is defined as the vertical space that is going
up and down the window.
• Letters
are used to designate each COLUMN'S location.
• In
the above diagram the COLUMN labeled C is highlighted.
• ROW
In a spreadsheet the ROW
• is
defined as the horizontal space that is going across the window.
• Numbers
are used to designate each ROW'S location.
• In
the above diagram the ROW labeled 4 is highlighted.
• CELL
In a spreadsheet the CELL
• is defined as the space where a specified row
and column intersect.
• Each CELL is assigned a name according
to its COLUMN letter and ROW number.
• In
the above diagram the CELL labeled B6 is highlighted. When
referencing a cell, you should put the column first and the row second.
• To Select a Range of Cells
– Move to the first cell in the range.
– The mouse pointer becomes a large cross.
– Click-and-hold the left mouse button and drag
left or right, up or down to the last cell you
want to select.
– Release the mouse button.
To Select All Cells in a Column or Row
• Click the gray Column heading to select the
entire column. (Click and drag the cursor across other column headings to
select those columns).
The gray Row heading to select the entire row. (Click and drag
the cursor down through the row
headings select those rows).
To Select the Entire Worksheet:
• Click the gray rectangle in the upper left
corner to select entire worksheet.
• If the cells and columns you want to select are not
directly next to one another, select one of the ranges you want to select, and
hold down the Control key while selecting other ranges.
• TYPES
OF DATA
In a spreadsheet there
are three basic types of data that can be entered.
a. labels
- (text with no numerical value)
b. constants
- (just a number -- constant value)
c. formulas*
- (a mathematical equation used to calculate)
*ALL
formulas MUST begin with an equal sign (=).
• LABELS
IN THE EXCEL
• Labels
are text entries.
• They
do not have a value associated with them.
• We
typically use labels to identify what we are talking about.
In our example: the
labels are:
Ø computer
ledger
Ø car
loan
Ø interest
Ø #
of payments
Ø Monthly
Pmt.
• CONSTANTS IN THE EXCEL
Constants
• are
entries that have a specific fixed value.
• If someone asks you how old you are, you would
answer with a specific answer. Sure, other people will have different answers,
but it is a fixed value for each person.
In our example: the constants are
• $12,000,
9.6% and 60
FORMULAS IN EXCEL
Formulas
are entries that have an equation that calculates the value to display.
We DO NOT type in the numbers we are looking for; we type in the equation. This equation will be updated upon the change or entry of any data that is referenced in the equation.
In our example, the solution was $252.61
are entries that have an equation that calculates the value to display.
We DO NOT type in the numbers we are looking for; we type in the equation. This equation will be updated upon the change or entry of any data that is referenced in the equation.
In our example, the solution was $252.61
This was NOT typed into the keyboard. The formula that was typed into the
spreadsheet
• FORMULAS
IN EXCEL cont..
BASIC FORMULAS IN EXCEL
• When
we are entering formulas into a spreadsheet we want to make as many references
as possible to existing data. If we can reference that information we don't
have to type it in again. AND more importantly if that OTHER information
changes, we DO-NOT have to change the equations.
• If
you work for 23 hours and make $5.36 an hour, how much do you make? We can set
up this situation using
• three
labels
• two
constants
• one
equation
Let's look at this
equation in B4:
• =
B1 * B2
• =
23 * 5.36
• Both
of these equations will produce the same answers, but one is much more useful
than the other.
DO YOU KNOW which is BEST and WHY?
DO YOU KNOW which is BEST and WHY?
• It
is BEST if we can Reference as much data as possible as opposed to typing
data into equations.
• FORMULAS IN EXCEL cont..
MATH BASIC FUNCTIONS
• Spreadsheets
have many Math functions built into them. Of the most basic operations are the
standard multiply, divide, add and subtract. These operations follow the order
of operations (just like algebra). Let's look at some examples.
For these following
examples let's consider the following data:
• A1
(column A, row 1) = 5
• A2
(column A, row 2) = 7
• A3
(column A, row 3) = 8
• B1
(column B, row 1) = 3
• B2
(column B, row 2) = 4
• B3
(column B, row 3) = 6
• FORMULAS IN EXCEL cont..
Mathematics basic functions
• SUM FUCTION
SUM FUCTION
• Probably
the most popular function in any spreadsheet is the SUM function. The Sum
function takes all of the values in each of the specified cells and totals
their values. The syntax is:
• =SUM
(first value, second value, etc)
• In
the first and second spots you can enter any of the following (constant, cell,
range of cells).
• Blank
cells will return a value of zero to be added to the total.
• Text
cells can not be added to a number and will produce an error.
















Social Plugin